Hyperbaric chamber therapy is a non-invasive medical procedure that raises the oxygen levels in your body. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) is the medical term for treating wounds that decompression sickness and carbon monoxide poisoning.
HBOT entails breathing while seated in a hyperbaric chamber, a confined environment with high-pressure oxygen. This increases the amount of oxygen that is flowing in your circulation by enabling your lungs to take in more oxygen.
The use of hyperbaric chamber treatment is examined in this article. It explains the conditions that HBOT cures and how it functions.
What is a Hyperbaric Chamber?
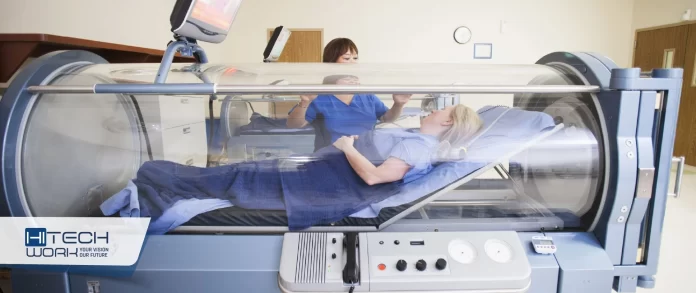
A hyperbaric chamber or HBOT chamber is an enclosed, highly pressurized area that is completely filled with oxygen. Hyperbaric chambers come in two varieties:
- Monoplace Hyperbaric Chambers: These clear acrylic tubes are made so that just one person may lie down or recline. Oxygen is pumped into the tube at high pressure.
- Multiplace Hyperbaric Chambers: These are pressurized spaces with many seats that are equivalent in size to an airplane cabin. High-pressure oxygen is given to each person through a mask or a thin, transparent hood that is put over the head.
In a hyperbaric chamber, the air pressure is two or three times higher than in a regular room. This enhances the absorption of oxygen and accelerates recovery.
What Is the Process of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
Recompression treatment, another name for hyperbaric chamber therapy, functions by supplying a regulated flow of oxygen, which is necessary for human survival. After being taken in by the lungs, oxygen moves via the bloodstream, the heart, and finally all of the body’s tissues.
High-pressure oxygen therapy, or HBOT, provides pure oxygen to the body, facilitating increased oxygen uptake for healing. Higher oxygen concentrations in the blood and other bodily fluids are therefore made possible as a result. Fluids high in oxygen go through several organ systems and aid in tissue healing.
For instance, following a stroke, increased oxygen levels in the cerebral spinal fluid—the fluid that envelops the brain and spinal column—might aid in the regeneration of neurones. Increased oxygen content in lymphatic fluid may support immune system function and aid in lymph node waste removal.
Advantages of a Hyperbaric Chamber
The blood’s ability to carry oxygen to the body’s damaged parts is disrupted by several diseases and traumas. To cure itself, the body need oxygen.
For instance, impaired circulation brought on by diabetes might hinder the ability of oxygen-rich red blood cells to reach injured tissue. As a result, wounds sustain an increased risk of infection and heal slowly.
Increased blood oxygen levels from HBOT are thought to benefit the body in the following ways:
- Aids in the bacterial death of immunological cells
- Lessens the inflammatory response
- Enhances collateral circulation, which is the development of new blood vessels that supply additional oxygen to afflicted regions.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a form of treatment that can be employed independently or to enhance the efficacy of drugs, including antibiotics.
Diseases Treated with Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment
Because HBOT raises oxygen levels in the tissues, it may be utilized to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries.
The following are some typical applications of hyperbaric oxygen treatment:
- A gas embolism in the arteries caused by air bubbles
- Inhaling harmful gasses can cause carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Toxicity from cyanide
- Decompression sickness is a frequent scuba diving disease.
- Particular varieties of wounds that don’t heal, like diabetic wounds
- A foul-smelling gas is released by gas gangrene, which spreads quickly in infected wounds.
- Cranial abscess (caused by an infection that started in the sinuses, ears, or some other major source)
- Radiation therapy-induced tissue injury
- Chronic infection of the bone marrow or bones: osteomyelitis
- Skin flaps or grafts that have compromised
- Severe anemia
- Brain abscess
- Burns
- Crushing injury
- Abrupt loss of hearing
- Unexpected, painless loss of sight
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Side Effects
While hyperbaric chamber therapy is thought to be a natural and safe therapeutic approach, there are certain adverse effects. These mostly impact the ears, sinuses, and lungs and are caused by variations in air pressure.
The following are possible minor, transient side effects of HBOT:
- Pressure or discomfort in the ears
- Popping of the ears
- Building up fluid in the middle ear
- Rare cases of lung collapse or barotrauma
- An eardrum rupture
- Pressure or discomfort in the sinuses
- Temporary alterations in eyesight that lead to nearsightedness
Try yawning or swallowing to pop your ears and relieve pressure in order to reduce issues with your sinuses and ears. In certain cases, ear tubes are implanted to lower pressure while receiving therapy.
How to Get Ready for Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
It’s imperative to take a shower before to an HBOT session. Stay away from wearing deodorants, perfumes, skincare items containing petroleum, and combustible hair products like hairspray.
At least four hours before to a session, avoid consuming any alcohol or fizzy beverages.
Because tobacco products obstruct the body’s natural capacity to transfer oxygen, smokers are recommended to give up when receiving treatment.
Prior to starting therapy, your doctor might enquire about the following:
- Do you feel like you have the flu, a cold, or nasal congestion?
- Are you feeling a fever?
- Are you expecting a child?
- Have you had anything to eat before the therapy?
- If you’re diabetic, did you take your medication before receiving it?
- Have you recently changed your prescription?
- Are you anxious?
Summary
Oxygen levels in your body can be raised with the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. The procedure entails laying down or sitting in a hyperbaric chamber, a high-pressurized space. Two hours or so make up a session.
Stealth burns, decompression sickness, and slow-healing wounds are all treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). Furthermore, although further studies are required to demonstrate its efficacy, it is utilized in alternative medicine to treat heart disease, depression, and neurological problems.
Air pressure variations can create sinus and ear pressure, although hyperbaric chamber therapy is often pleasant and calming. Ruptures of the eardrum, lung collapse, and oxygen poisoning are uncommon side effects of HBOT.